
Stomach part01
23.4 The Stomach Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the functional anatomy of the stomach Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself
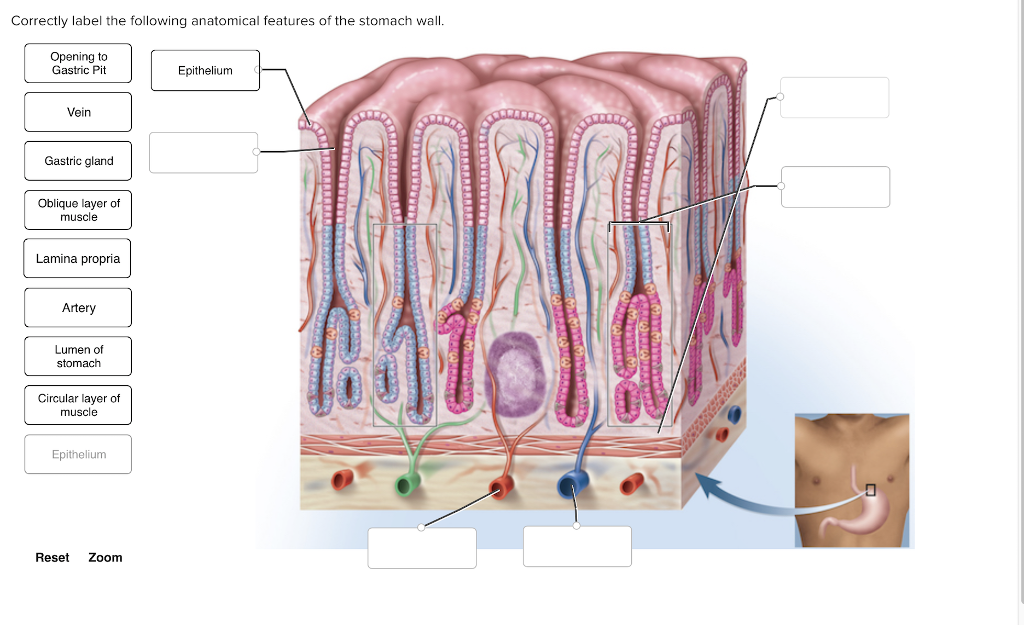
Solved Correctly label the following anatomical features of
The stomach is a sac-like organ with strong muscular walls. In addition to holding food, it serves as the mixer and grinder of food. The stomach secretes acid and powerful enzymes that continue.

Stomach Anatomy Illustration Stock Vector Illustration of biology, medicine 194368838
Anatomy of the Stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper belly (abdomen). It's part of the digestive system. It's between the end of the food pipe (esophagus) and the start of the first part of the small bowel (duodenum). The stomach is much like a bag with a lining. The stomach is made of these five layers: Mucosa.
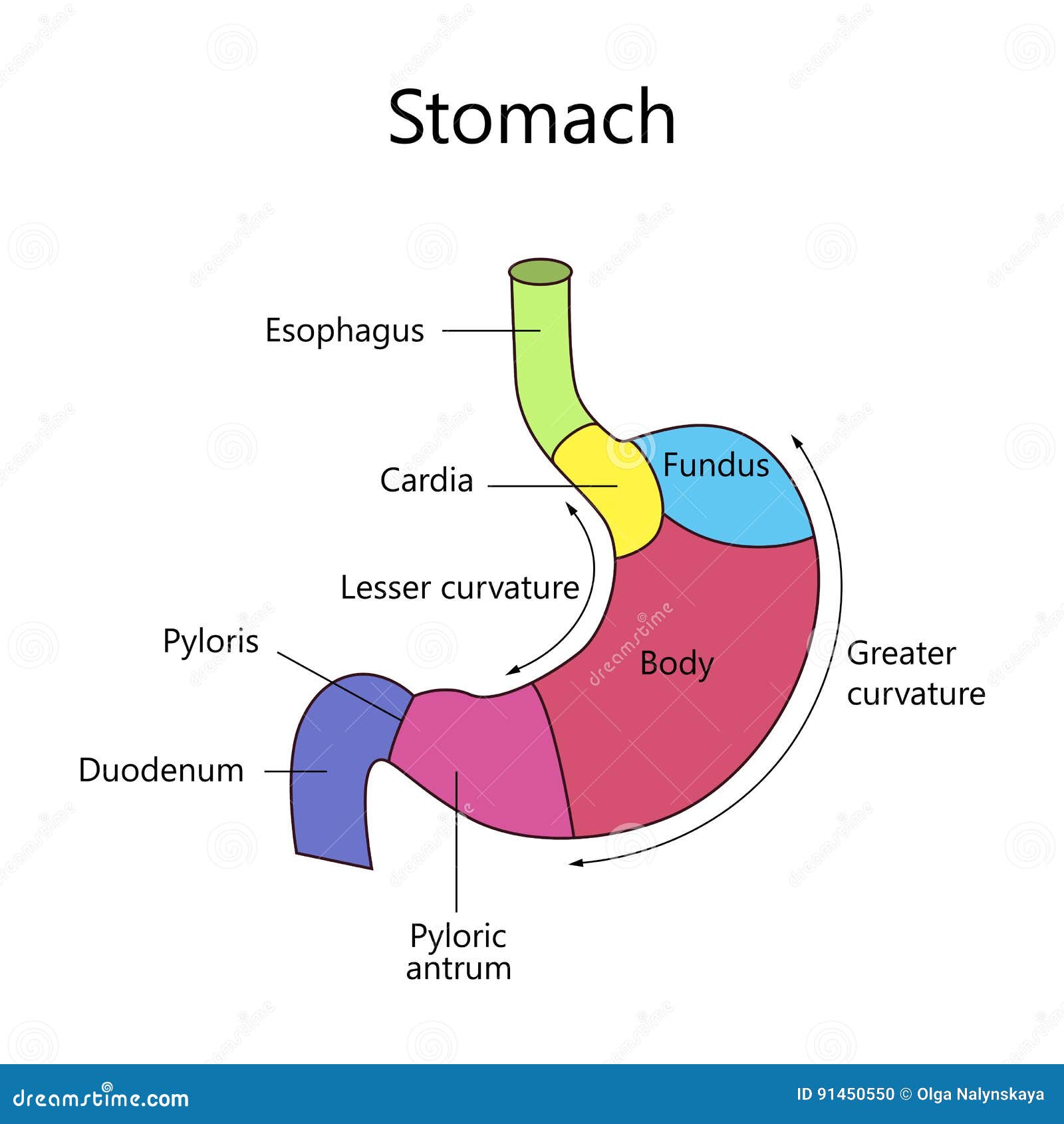
Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medical, antrum 91450550
The stomach is a muscular organ that is found in our upper abdomen. If we were to locate it on our bodies, it can be found on our left side just below the ribs. In simple terms, the stomach is a kind of digestive sac. It is a continuation of the esophagus and receives our churned food from it. Therefore, the stomach serves as a kind of.

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
Label on a diagram the four main regions of the stomach, its curvatures, and its sphincter Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself Describe the mechanical and chemical digestion of food entering the stomach

The Anatomy of the Abdomen Human Stomach Health Life Media
Stomach, saclike expansion of the digestive system, between the esophagus and the small intestine; it is located in the anterior portion of the abdominal cavity in most vertebrates. The stomach serves as a temporary receptacle for the storage and mechanical distribution of food before it is passed into the intestine.
The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
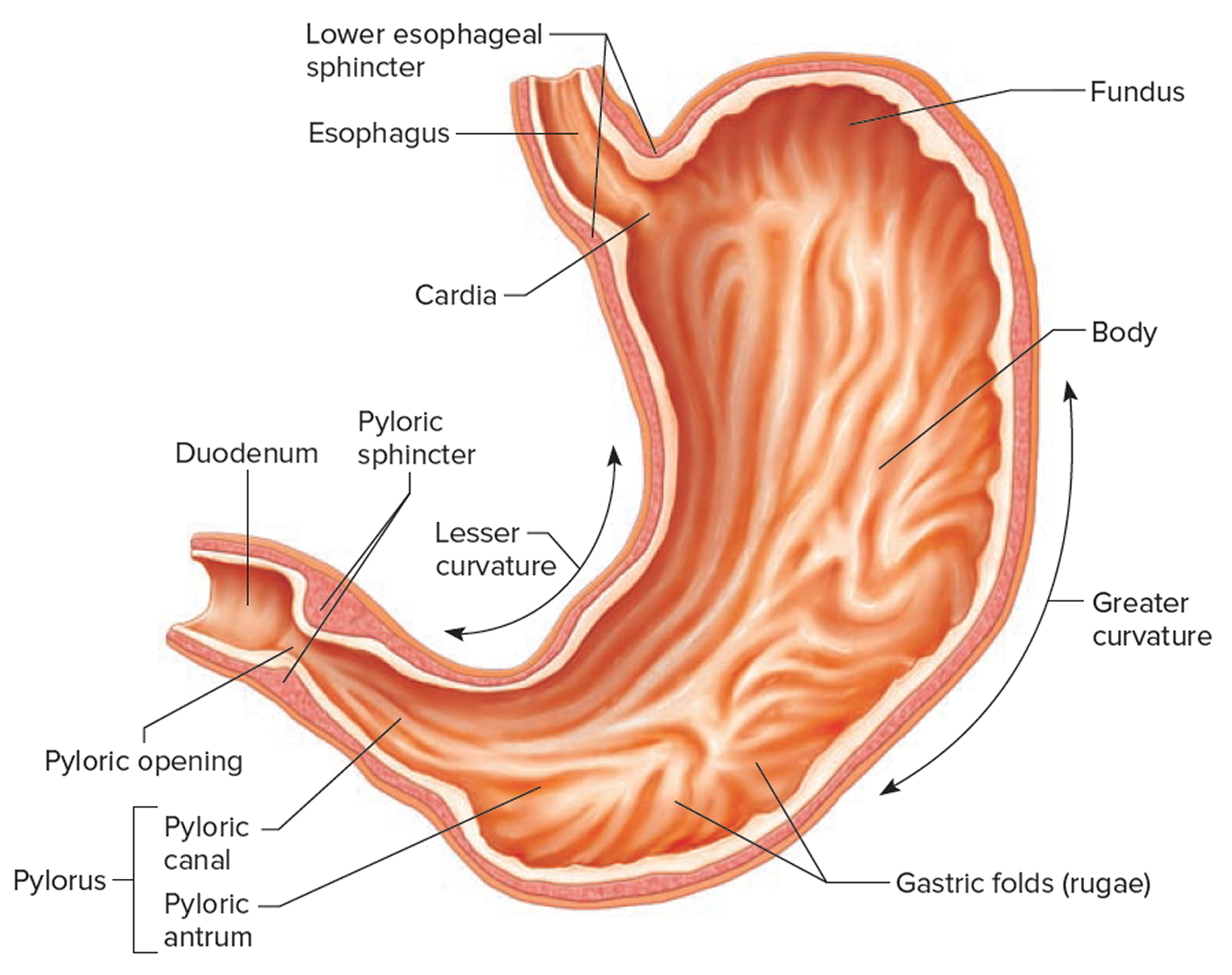
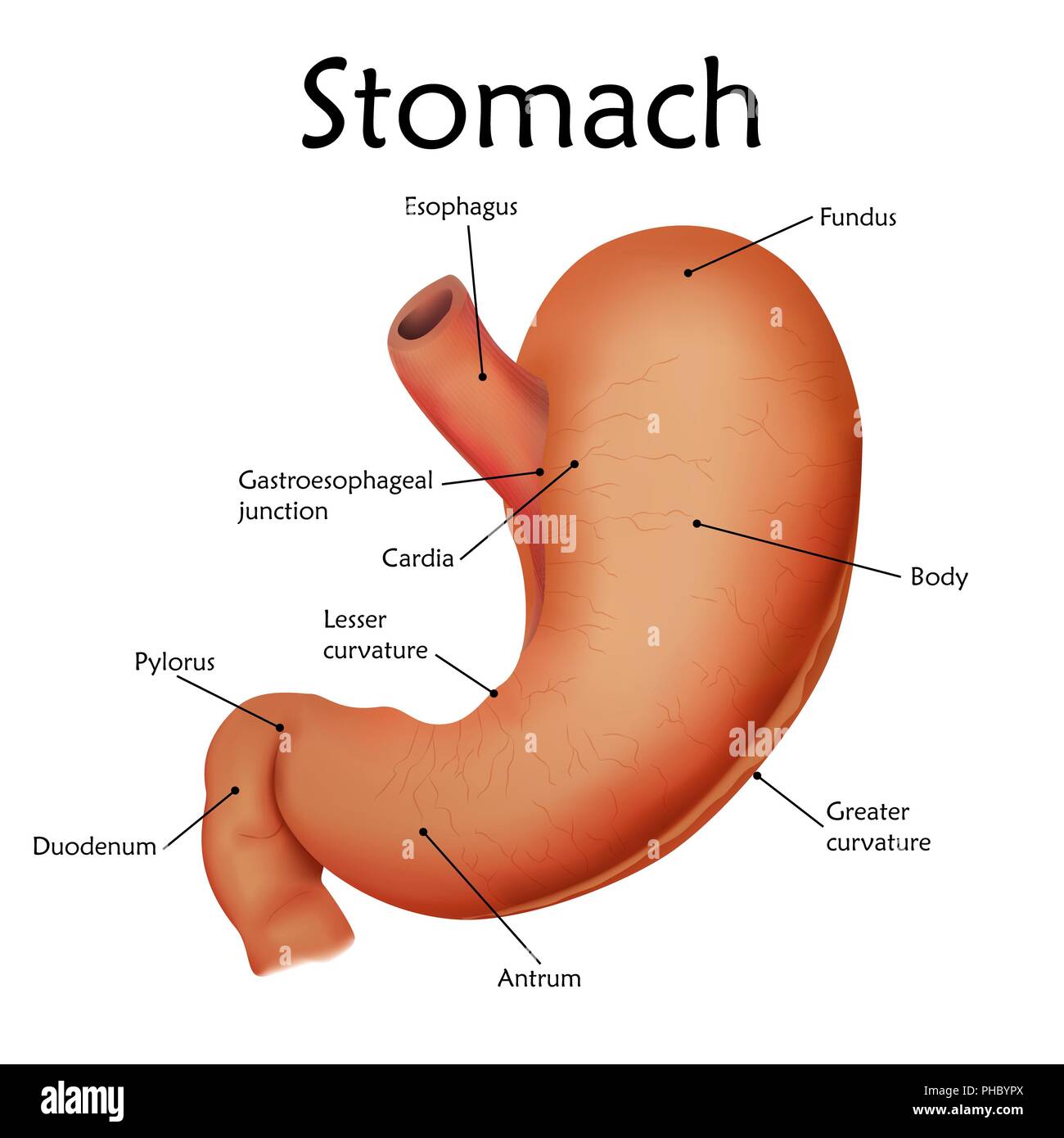
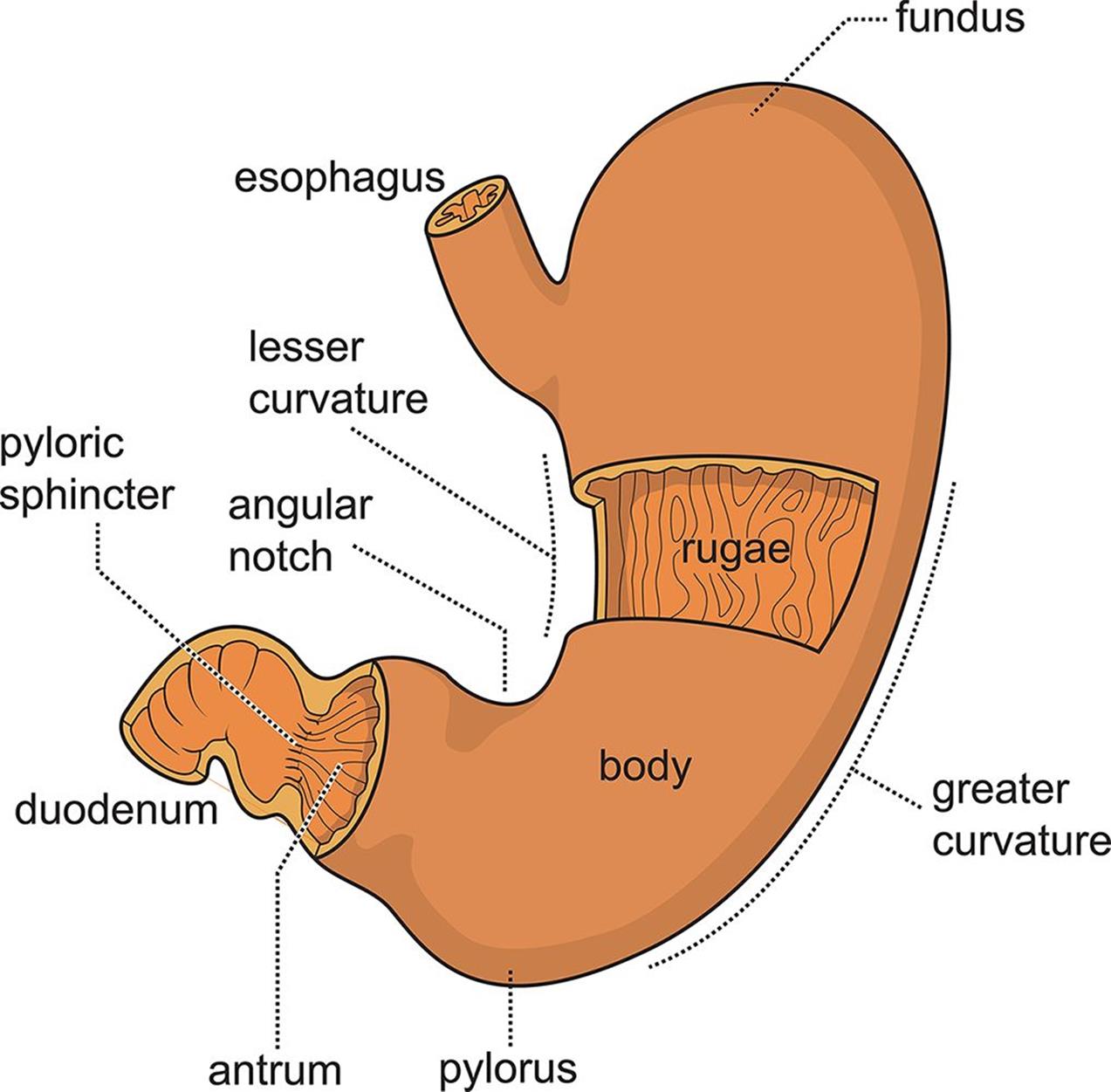
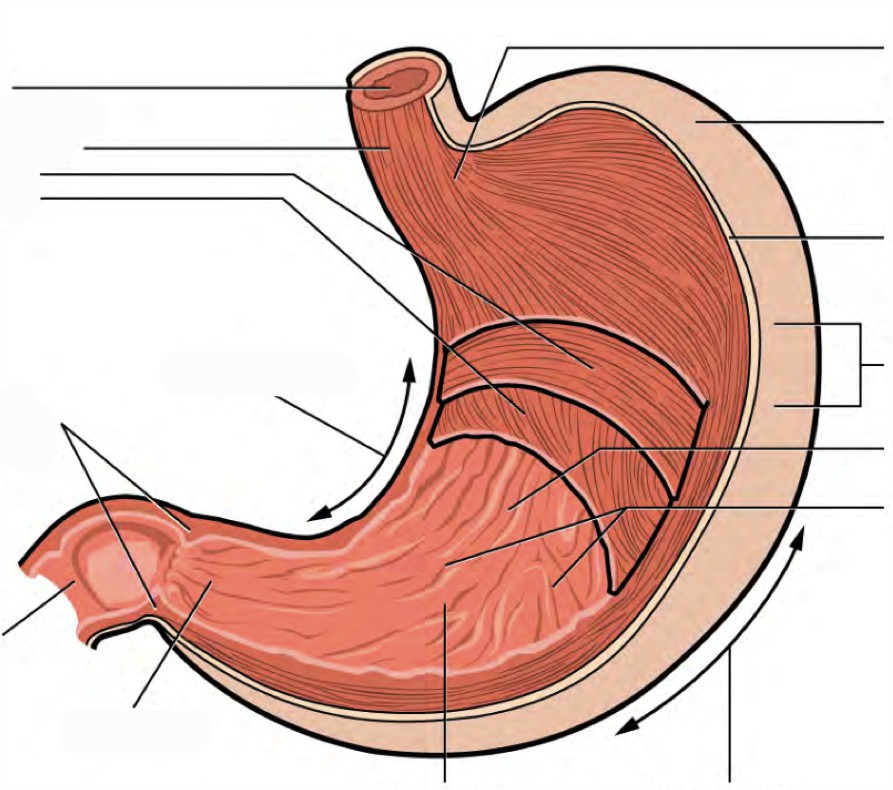
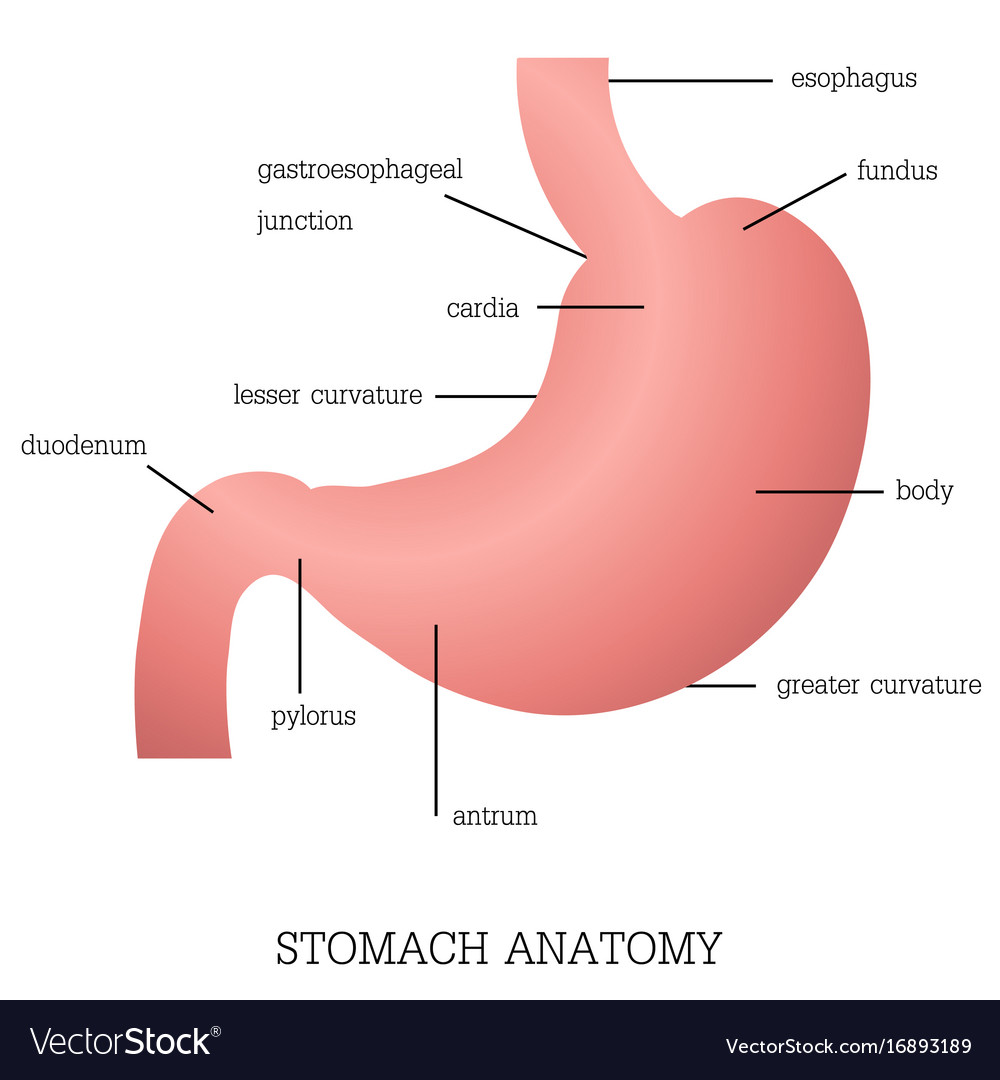
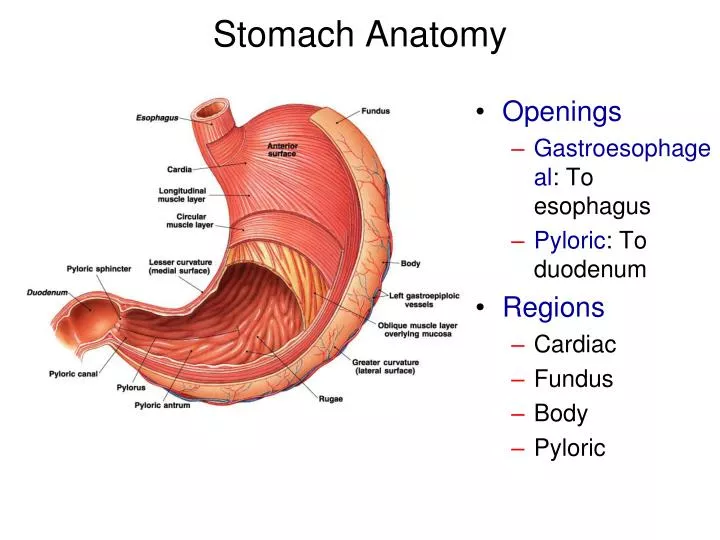
The stomach has four major regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The addition of an inner oblique smooth muscle layer gives the muscularis the ability to vigorously churn and mix food. The convex lateral surface of the stomach is called the greater curvature; the concave medial border is the lesser curvature.
Human stomach with labels, illustration Stock Photo Alamy
What is the stomach? The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. It produces enzymes (substances that create chemical reactions) and acids (digestive juices). This mix of enzymes and digestive juices breaks down food so it can pass to your small intestine. Your stomach is part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Ingestion and Digestion The Digestive System MCAT Biology Review
Stomach histology Author: Egle Pirie BSc (Hons) • Reviewer: Nicola McLaren MSc Last reviewed: October 30, 2023 Reading time: 13 minutes Recommended video: Stomach histology [29:47] Have a thorough look at stomach under the microscope. Body of stomach Corpus gastris 1/5 Synonyms: Gastric body, Corpus of stomach , show more.
PreLab 8 Human Anatomy Lab Manual
The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food. Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus .

Inside of the Stomach The Comical Anatomist
Digestive system diagram Yaja' Mulcare The digestive organs in the abdomen do not work alone. They depend on organs in the mouth and chest, such as the esophagus and tongue, to help chew, move.

Simple stomach diagram Stomach structure Stomach Anatomy Stomach diagram, Digestive system
From Marieb et al., Human Anatomy, 7th edition, Pearson, 2014. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a single tube, extending from the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus, through the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, ending in the rectum and anus. Each segment of the GI tract is regionally specialized for particular digestive functions.
Barrio Lechuguilla papi stomach anatomy diagram Productividad en un día festivo Jugando ajedrez
Given below is a labeled diagram of the stomach to help you understand stomach anatomy. The stomach is divided into four parts. These include: Cardia Fundus Body Pylorus Cardia refers to the section of the stomach that is located around the cardiac orifice. The lower esophageal sphincter lies at the junction where the esophagus meets the stomach.

Human Stomach Anatomy Vector Illustration With Labels Stock Illustration Download Image Now
Label the Stomach by bloomerwirchball 53,202 plays 15 questions ~40 sec English 15p More 71 3.89 (you: not rated) Tries 15 [?] Last Played December 18, 2023 - 11:29 PM There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Remaining 0 Correct 0 Wrong 0 Press play! 0% 08:00.0 Other Games of Interest
PPT Stomach Anatomy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1940155
Anatomical Structure Divisions of the Stomach The stomach has four main anatomical divisions; the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus: Cardia - surrounds the superior opening of the stomach at the T11 level. Fundus - the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia. Body - the large central portion inferior to the fundus.

stomach model Anatomy models labeled, Anatomy models, Human anatomy and physiology
The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this.